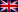
Achieved Targets: Published Releases and Features of psiKeds
(C* = Complexity | R* = Responsible | P* = Priority / success)
| Label | Task | Specification | C* | R* | P* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
gold release :- prefinal psiKeds release 0.90.1 | Q4/15 | ||||
| PBL-zNN | |||||
silver release :- enhanced psikeds release 0.9.8 | Q2/15 | ||||
| PBL-yNN | |||||
techneticum release :- refactoring release 0.9.7 | Q4/14 | ||||
| PBL-xNN | |||||
brass release :- first really usable psiKeds release 0.9.6 | Q2/14 | ||||
| PBL-c12 | Logging the list of decisions as base for a reset / undo to solve conflicts and erroneous decisions | The deduction protocol shall not only allow to prescribe a partial solution (aktueller Wissenstand) which the next deduction step has to respect as ist context, but also a set of decisions, which must be respected during the deduction. | M | MJ | ✔ |
| PBL-c11 | Enhanced complex knowledge base | The XSD, the xtext editor, and the knowledge machine is prepared to contain even complex knowledge bases using the recently achieved expressive power | L | KR | ✔ |
| PBL-c10 | Simple number of PS / components | The knowledge base shall be able to express that a PV has n * constituting PS as 'components'. Thee simple interpretation is, that the one selected fulfilling PV is added n times. | S | MJ | ✔ |
| PBL-c09 | Xtext based knowledge base editor (for xml psiKeds knowledge bases) | Instead developing psiKeds knowledge bases directly by using an xml Editor the psiKeds knowledge base language shall be taken as domain specific language and defined by Xtext. (Ironically, the specific domain is then the domain of domain independent psiKeds knowledge representations) | XL | KR | ✔ |
| PBL-c08 | simple psiKeds knowledge base format | New knowledge base format, which does not use xml as meta format, is defined | XL | KR | ✔ |
| PBL-c07 | Functions on feature events | Function rules are operating on feature class events which use values of type number. Function rules take n prefix arguments (events) and compute the value of one conclusio feature class event. Reverse Computing ('Modus Tollens') is also possible. | XL | MJ | ✔ |
| PBL-c06 | Logical rules on concept events and concept NOT events | Events and NOT events on concepts shall be usable as parts of logical rules. | M | MJ | ✔ |
| PBL-c05 | Events and NOT events on concepts | Following the idea of the variant and feature events, events shall also be able denote specific concepts. | M | MJ | ✔ |
| PBL-c04 | Feature sets as concepts | A set of features which sub-specifies a variant is taken as a concept and integrated into a variant specific is-a concept taxonomy. | L | MJ | ✔ |
| PBL-c03 | Relations on features (= feature values [strings | numbers]) | The use of the (reversable) relations <, >, =, <> shall be enabled. Relational expressions refer to [ <, >, =, <> ([context sensitive prefix + Fclass],([context sensitive prefix + Fclass])]. Reverse triggering ('Modus Tollens') | L | MJ | ✔ |
| PBL-c02 | Logical rules on NOT events (on variants and features) | A NOT Event shall become true, if inside of a happened context sensitive prefix a purpose variant or a feature value has not been selected. | M | MJ | ✔ |
| PBL-c01 | Logical rules on feature events (= feature values [strings | numbers] for sub-specifying variants) | Events shall denote specific feature values. PVs contain lists of allowed FVals. Each FVals of such a list belongs to the same feature class. An event id: [context sensitive prefix + PV + FClass + FValue]. Logical rules work just as those of PV-Events. | M | MJ | ✔ |
copper release :- first published stable psiKeds release 0.4.0 | Q4/13 | ||||
| PBL-b09B | Implementing a basic demo reference database | Based only on variant events, the 'web-server-environment' is written as psiKeds xml database and can be evaluated by the resolution engine for inferring valid knowledge entity descriptions. The results are successfully demonstrated. | M | MJ | ✔ |
| PBL-b09A | Specifying some basic reference database | The 'eimer'-domain and the 'web-server-environment' are defined as basic reference domains | M | KR | ✔ |
| PBL-b08B | Implementing the initial version of the resolution / inference process | The inference machine of the resolution engine evaluates logical rules based on variant events and derives knowledge entity descriptions by using the Modus Ponens and the Modus Tollens as conclusion pattern | XL | MJ | ✔ |
| PBL-b08A | Specifying the initial version of the resolution / inference process | Operating on variant events and (simple) logical if-then-rules, the resolution engine takes a decision and computes the next state of the knowledge entity description: (A) The selected variant [decision] is added to the description. (B) The logical conclusions are computed: (a) If the decision makes the context of an event happened, its detail is marked as relevant. (b) If the decision makes the context of an event unhappened, the event is marked as irrelevant. (c) Irrelevant events let the rules become fulfilled. (d) If the decision makes the premise of a rule true, the variant of the conclusion is automatically added as component. [Modus Ponens] (e) If the decision makes the conclusion of a rule false, the variant of the corresponding premise is automatically excluded from the set of possible decisions [Modus Tollens]. (f) Conclusions of the automatically computed conclusions are computed too. (g) If there can still only be selected one variant, it is automatically selected and evaluated like a manual (external) decision. | L | KR | ✔ |
| PBL-b07B | Implementing the resolution protocol into the client:server component | The query agent can deal with the protocol definition, especially it is enabled to store the already known part of the knowledge entity description and to add it into the resolution dialogue automatically, if the resolution engine requests for such a description. | L | MJ | ✔ |
| PBL-b07A | Implementing the resolution protocol into the server:server component | The resolution engine can deal with the protocol definition. Additionally, it manages a set of indicators triggering the destroy of an in-memory-deduction. To manage these indicators includes to respect a configurable strategy to destroy the oldest / largest / rarely used in-memory-deduction. | XL | MJ | ✔ |
| PBL-b06 | Specifying the resolution dialogue (protocol) as a set of stateless re-entrant communication points | The resolution / deduction dialogue is defined as a set of independent resolution steps. Besides the decision, which shall be respected by the resolution engine, each single request contains either a session id or a (partially deduced) description of a knowledge entity (object) as a reference to the 'already known part of the entity'. If the resolution engine gets a session id, it tries to map the session number to the corresponding in-memory-deduction. If this (still) does not exist (any longer) the resolution engine requests for the corresponding entity description. If the resolution engine gets an entity description, it re-initializes the in-memory-deduction. Based on the found / re-initialized in-memory-deduction and the prescribed decision, the resolution engine computes and delivers the next state of the knowledge entity description. The protocol must allow the resolution engine to destroy any in-memory-deduction whenever the it wants to free memory. | M | KR | ✔ |
nickel release :- initial subsequently published psiKeds release 0.1 | Q2/13 | ||||
| PBL-b05b | Making the flat test domain requestable | The query agent can request for a knowledge entity description, the resolution engine can deliver a syntactically valid description without logically inferring its internal elements, and the query agent can present the result. | L | MJ | ✔ |
| PBL-b05a | Making the flat test domain loadable | The resolution engine can read, understand, and load the reference domains | M | MJ | ✔ |
| PBL-b04 | Setting up the psikeds environment as a java based framework | The resolution engine is set up as a java server:server application being executable by tomcat and different java runtime engines (java 7, java 8, and open-jdk-7). The query agent is implemented as a java based client:server engine: (a) As client it sends queries to the resolution engine and gets json based answers using the http protocol. (b) As server, the client:server gets requests by an html interface running in a browser and delivers new (elements of the) html pages. These applications are developed by using the maven development process; the source code is developed by using the eclipse environment. | XL | M | ✔ |
| PBL-b03 | Specifying a flat test database | The 'chocolate'-domain is defined as simple reference domain. | M | MJ + KR | ✔ |
| PBL-b02 | Implementing the XSD for psiKeds XML databases | The psiKeds resolution engine is enabled to verify databases by an XSD and to accept only valid databases. | S | MJ | ✔ |
| PBL-b01 | Specifying the psiKeds XML database format | An xml psiKeds knowledge bases first defines the basic elements (variants, purposes, features) as members of lists. Each member can be referred by a specific identifier. Based on these identifiers, it defines the and-or-purpose-variant-graph, the events, and the event based (logical) rules. | L | KR | ✔ |